- About
- Solutions
- Essentials
- Utilities
- Publications
- Product Delivery
- Support
Integrate Data for Competitive Advantage
Over time, the number of legacy applications developed to support an enterprise’s operations grows significantly. Applications maintain databases of information, but the database contents are not typically exposed for use by other independently developed applications.
As companies grow more reliant on their IT resources, it is apparent that many are storing data in silo legacy databases. As companies merge, it is often necessary to join disparate databases into a common repository for the new corporation.

Integrate heterogeneous databases with HPE Shadowbase Data and Application Integration for a Multi-database Solution
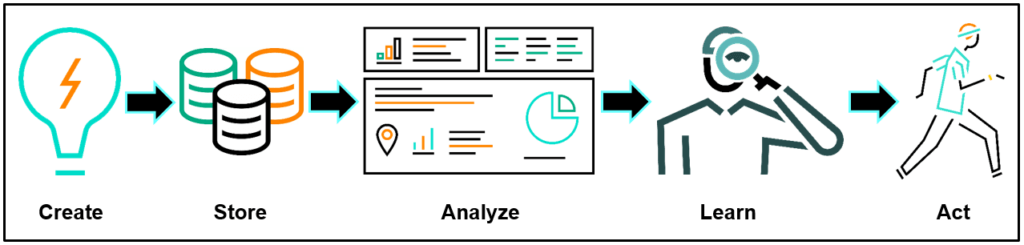
From onset to action, there is value in data. The Data Continuum represents data’s typical lifecycle:
Companies that record and analyze data about their business can analyze their performance, which can help determine the next action to take.
Application capacity defines how many users an IT application service can support in a given response time. Another critical factor is the application’s ability to scale, which is dependent upon the application’s architecture.
The two most important scaling factors for an application are increasing the number of users that can be processed:
Scaling up usually consists of replacing existing hardware with more powerful versions, whereas scaling out usually consists of adding more processing power by spreading the load across multiple environments. Scaling up is often limited by the maximum capacity that a single monolithic environment can achieve.
The amount of information being generated each year is exploding at an unprecedented rate. It is estimated that 80% of the world’s data was generated in the last two years, and this rate is increasing. Social media such as Twitter and Facebook, articles and news stories posted online, blogs, emails, YouTube and other videos are all contributing to big data.
In today’s 24×7 online environment, having query access to a remote database is not sufficient. Querying for data is a lengthy and complex process, and applications must react far more quickly to data changes than querying allows. A data pipeline can be created here to parse data from a data pump.
HPE Shadowbase solutions play a pivotal role in integration of the cloud with private (internal) IT infrastructure, allowing for hybrid approaches that assign critical processing to highly available private systems such as HPE NonStop Servers (among others), and noncritical processing to the public cloud.
Shadowbase software can transform the data between source and target database formats either automatically or via Shadowbase User Exit customizations. Data may be aggregated, disaggregated, and/or transformed.
Applications that once were isolated can now interoperate at event-driven level in real-time. Critical data generated by one application is distributed and acted upon immediately by other applications, enabling the implementation of powerful Event-Driven Architectures (EDA).
Several production use cases are included that illustrate how this data distribution technology brings new opportunities and value to various enterprises.
What is needed is a way for one application to immediately have real-time access to the data updated by another application, just as if that data were stored locally. Furthermore, big data analytics engines require a large network of tens, hundreds, or even thousands of heterogeneous, purpose-built servers, each performing its own portion of the task.
Since these systems must intercommunicate with each other in real-time, they must share an integrated high-speed, flexible, and reliable data distribution network.
Learn More About Shadowbase Streams