- About
- Solutions
- Essentials
- Utilities
- Publications
- Product Delivery
- Support
Business continuity (or business reliance or business continuance) encompasses the activities that an enterprise performs to maintain consistency and recoverability of its data, operations, and services.
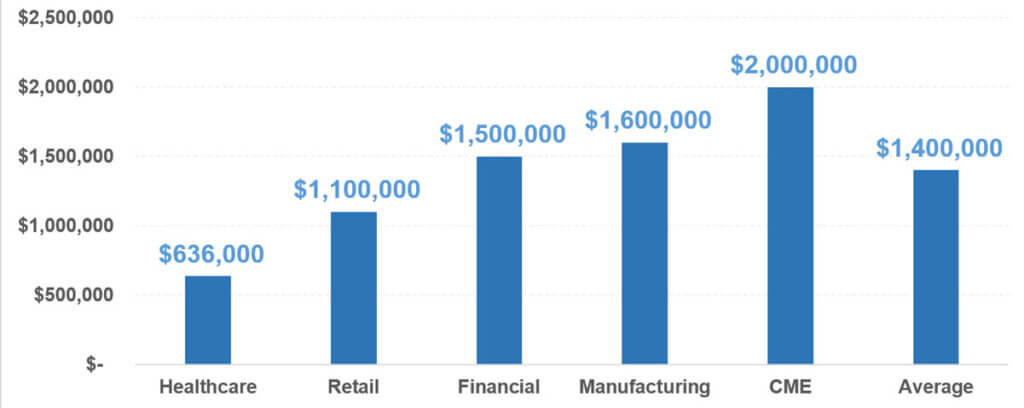
Figure 1 — Average Cost of Downtime per Hour by Industry (in $US)
Figure 1 states the numerous costs per hour of downtime by industry: healthcare loses $636K, retail $1.1M, financial $1.5M, manufacturing $1.6M, and Communications/Media/Entertainment $2M, with the average at $1.4M. (Source: Network Computing, the Meta Group, Contingency Planning Research.)
The IDC defines four Availability Levels (ALs), AL1 – AL4, for classifying downtime. Each level corresponds to the number of 9s in the average availability after the decimal point. It also calculates the average cost of downtime for each level from the “Average Cost of Downtime per Hour” in Figure 1 (note: $1.4M USD per hour equals $388.88 USD per second, on average). Note that Shadowbase business continuity architecture satisfies the most demanding ALs (AL2 – AL4).
| Table 1 — IDC Availability Levels | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Availability Level (AL)1 | Shadowbase Architecture | User Notice Ability | Yearly Downtime2 | Yearly Cost (USD) | |
| AL1: 99.9% | N/A | All work stoppage, uncontrolled shutdown | 08:45:56 | $1,227,149.73 (USD) | |
| AL2: 99.99% |
Active/Passive |
User interruption, performance degradation, in-flight transaction interruptions | 00:52:35 | $122,714.97 (USD) | |
| AL3: 99.999% |
Sizzling-Hot-Takeover |
Performance degradation, automatic failover transfers | 00:05:15 | $12,271.50 (USD) | |
| AL4: 99.9999% |
Active/Active |
None | 00:00:31 | $1,227.15 (USD) | |
| 1Source: IDC Publishes High Availability Survey 2Note: “Yearly Downtime” is expressed in hours (HH), minutes (MM), and seconds (SS) timestamp format: HH:MM:SS. |
|||||
RTOs of minutes to seconds is considered high availability, while RTOs of seconds to sub-seconds is considered continuous availability.
The inability to access or update current data carries a significant business cost, possibly measured in many thousands of dollars per second.
Note, companies already know that they need to specify their datacenters’ availability in terms of their RPO and RTO. We argue that companies also need to know their:
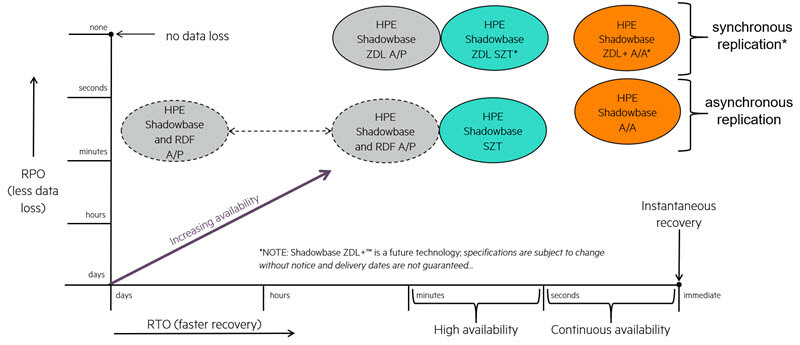
Figure 2 — The HPE Shadowbase Business Continuity Continuum (BCC)
*Note: Shadowbase ZDL architectures are future synchronous technologies; specifications are subject to change without notice, and delivery dates are not guaranteed.
In Figure 2, AL and the amount of data loss in each architecture improves as you move from the lower left to the upper right: horizontally from an active/passive through sizzling-hot-takeover (SZT) to an active/active architecture, and vertically from asynchronous to synchronous data replication technology.
The overall return on investment in deploying a Shadowbase business continuity solution is positive, by preventing prolonged periods of downtime or data loss which can cost a business thousands or even millions of dollars.
HPE Shadowbase data replication solutions support low-latency, uni-directional, and bi-directional data replication between homogeneous and heterogeneous systems and databases with scalability, selectivity, and sophisticated data transformation and mapping facilities, therefore providing a business continuity solution to meet any business requirement.
Uni-directional active/passive disaster recovery for high availability.
Shadowbase DCR automatically replicates and applies SQL/MP SQLCI (DDL) source commands to the target database. It automatically adjusts the source command to match the target environment’s details (e.g., file / table name mapping).
SQLCI DDL commands integrate with HPE Shadowbase (DML) real-time replication. It is particularly helpful to customers migrating from RDF / SDR to HPE Shadowbase.
Discover HPE Shadowbase DDL Command Replication (DCR)HPE NonStop Pathway is an application framework that is a mainstay of mission-critical online transactional processing (OLTP) systems.