Real-Time Fraud Detection and Resolution for Financial Switch
Share This!
 Copy link to clipboard
Copy link to clipboard Email link
Email link Print
Print
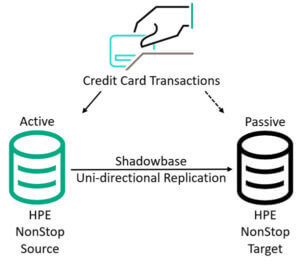
Figure 1 – Shadowbase Disaster Recovery (DR) Architecture
Situation
One of the largest U.S. processors of credit card transactions provides transaction authorization and settlement services for thousands of attached devices using a home-grown application on a pair of HPE NonStop systems.
The processor recently upgraded its servers and implemented an HPE Shadowbase Disaster Recovery architecture (Figure 1).
Problem
- The processor wanted to add additional servers and distribute them around the U.S. for disaster tolerance while efficiently utilizing these servers’ capacity.
- Additionally, fraudulent transaction activity was increasing and costing the processor a great deal of money.
- The processor needed to integrate real-time fraud detection into its transaction authorization services to identify suspicious activity.
- Directly modifying the authorization application processing would involve extensive and complex changes and require a lengthy testing cycle.
Solution
- Use HPE Shadowbase bi-directional data replication for business continuity to synchronize application databases in a “route anywhere” model (any user/transaction can be serviced by any system, Step 1).
- Use HPE Shadowbase Data and Application Integration to bi-directionally integrate the authorization activity in real-time with an off-platform fraud detection solution from Fair Isaac (Step 2).
Additional Notes About this Architecture
Since the databases are kept synchronized via asynchronous replication, data collisions can occur. As a request is received, it is applied and the application updates the record’s “update-timestamp” field, and then the change is asynchronously replicated to the other node so that all copies of the database are kept up-to-date.
When data collisions occur (due to the nature of asynchronous replication), they are automatically resolved by a predetermined algorithm, which looks at a request’s record contents and applies the request with the most recent update timestamp (the other change loses and is logged to a reject log for record).
Note: HPE Shadowbase software supports other data collision resolution algorithms such as choosing the highest or lowest value of a specified field, or choosing the earlier update, depending on the underlying application’s need.
Outcomes
- Improves the processor’s BC architecture – upgrades the application availability to a continuous availability architecture, enables efficient utilization of server capacity, and improves system scaling by integrating with multiple geographically-dispersed fraud detection systems
- Incoming requests are load-balanced by assigning them to a server with the least workload
- Integrates the NonStop-based authorization application with the Linux-based fraud detection solution without requiring code changes to either
- Identifies and suspends suspicious transactions before authorization occurs
- Dramatically reduces costs of fraudulent activity
HPE Shadowbase Products of Interest for Business Continuity (Step 1 above)
- HPE NonStop Shadowbase Basic Replication Software (BE441AC/QSA49V6)
- HPE NonStop Shadowbase Advanced Replication LTU (BE442AL/QSA50V6)
- HPE NonStop Shadowbase Compare Software (BE445AC/QSA53V6) (not shown but recommended)
HPE Shadowbase Products of Interest to Support Real-time Fraud Detection (Step 2 above)
- HPE NonStop Shadowbase Basic Data Integration Software (BE443AC/QSA51V6)
- HPE NonStop Shadowbase Advanced Data Integration LTU (BE444AL/QSA52V6)
- HPE NonStop Shadowbase Essentials Software (BE446AC/QSA54V6)
- HPE Shadowbase Basic Application Software 1-8 core or 9+ core (WSA51V6T1/T2)
- HPE Shadowbase Advanced Application Software LTU 1-8 core or 9+ core (WSA52V6T1/T2)
Contact us or your HPE Shadowbase representative, and learn how Shadowbase software will benefit you.
Further Reading
Related Case Study:  Payment Authorization — A Journey to Continuous Availability
Payment Authorization — A Journey to Continuous Availability
Related White Papers:


![]() Payment Authorization — A Journey to Continuous Availability
Payment Authorization — A Journey to Continuous Availability